Сурет:Fasciola LifeCycle.gif
Fasciola_LifeCycle.gif (568 × 435 пиксел, файл өлшемі: 58 КБ, MIME түрі: image/gif)
Файл тарихы
Файл сол кезде қалай көрінгенін көру үшін күн/уақыт дегенге басыңыз.
| Күн/Уақыт | Нобай | Өлшемдер | Қатысушы | Пікір | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| қазіргі | 01:05, 2015 ж. шілденің 10 |  | 568 × 435 (58 КБ) | CFCF | updated |
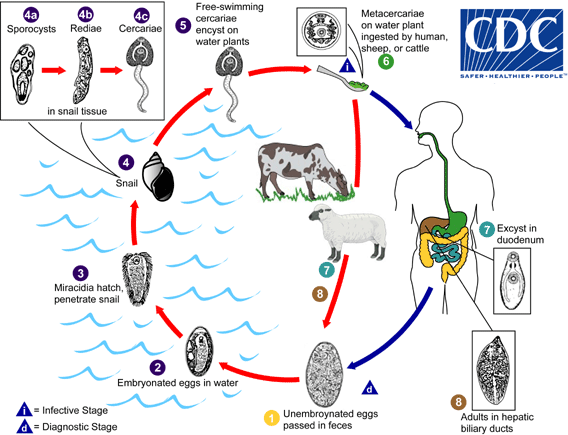
| 22:59, 2006 ж. мамырдың 10 |  | 568 × 435 (45 КБ) | Patho | {{Information| |Description=Causal Agents: The trematodes Fasciola hepatica (the sheep liver fluke) and Fasciola gigantica, parasites of herbivores that can infect humans accidentally. Life Cycle: Life cycle of Fasciola hepatica Immature eggs are disch |
Файл қолданылуы
Бұл файлды мына бет қолданады:
Глобалды файл қолданылуы
Бұл файл келесі басқа уикилерде қолданылады:
- ca.wikipedia.org жобасында қолданылуы
- ceb.wikipedia.org жобасында қолданылуы
- cs.wikipedia.org жобасында қолданылуы
- de.wikibooks.org жобасында қолданылуы
- es.wikipedia.org жобасында қолданылуы
- fr.wiktionary.org жобасында қолданылуы
- gl.wikipedia.org жобасында қолданылуы
- gl.wiktionary.org жобасында қолданылуы
- hi.wikipedia.org жобасында қолданылуы
- it.wikipedia.org жобасында қолданылуы
- ru.wikipedia.org жобасында қолданылуы
- se.wikimedia.org жобасында қолданылуы
- sv.wikipedia.org жобасында қолданылуы
- vi.wikipedia.org жобасында қолданылуы
- vi.wiktionary.org жобасында қолданылуы